
The Lasting Impact of Soil Remediation
Introduction
Soil contamination is an escalating problem that poses severe threats to both the environment and human health. Traditional remediation techniques, such as excavation and off-site disposal, often come with high costs and significant environmental footprints. In contrast, In-Situ Soil Remediation stands as a robust method to treat contaminated soil without removing it from its original location, offering advantages like cost-effectiveness and minimal environmental impact.
Types of In-Situ Soil Remediation Techniques
Biological Treatment
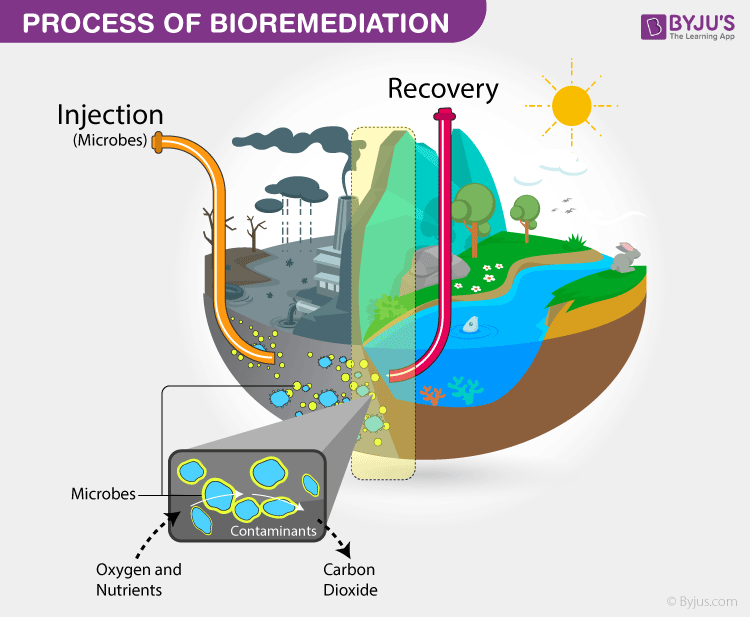
Bioremediation and bioventing are examples of biological treatment techniques that leverage microorganisms to break down contaminants into less harmful or non-toxic substances.
Chemical Treatment
Examples include chemical oxidation, chemical reduction, and soil flushing. These methods can be highly effective but may require careful management to minimize secondary environmental impacts.
Physical Treatment
Physical treatment methods like soil vapor extraction and air sparging focus on the separation or containment of the contaminants.
Factors to Consider
Site Characteristics
Physical attributes such as soil type, depth of contamination, and groundwater conditions must be considered.
Contaminant Properties
The type, concentration, and distribution of contaminants will influence the choice of remediation technique.
Regulatory Requirements
Compliance with local, regional, or national environmental laws is non-negotiable.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- Lower costs
- Minimal environmental disruption
- Faster implementation
Limitations
- Not suitable for all types of contaminants
- Risk of incomplete or uneven treatment
- Potential for secondary pollutants
| Sampling Date | TPHg | Benzene | Toluene | Ethylbenzene | Total Xylenes | MTBE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pre-bioaugmentation | 10/6/09 1 | 200 | 320 | 7.2 | 700 | 70 | 5 |
| post-bioaugmentation | 4/26/10 | <50 | <0.5 | <0.51 | <1 | <5 | <0.5 |
Innovations in the Field
Enhanced Bioremediation
Techniques are now available to stimulate the growth of naturally occurring microorganisms, accelerating the degradation process.
Bioaugmentation Applications
Innovations like the use of specifically cultured bacteria, such as Pseudomonas Fluorescens, offer a targeted and effective treatment method.
Conclusion
In-Situ Soil Remediation is not just a method; it’s a necessity for sustainable environmental management. As we grapple with the growing environmental concerns, the role of in-situ soil remediation in safeguarding our natural resources becomes ever more critical.
Contact Us
For more information, please feel free to contact us at Delta Remediation.
Email: INFO@DELTAREMEDIATION.COM
Phone: +1 780 962 7991
Copyright © 2023 Delta Remediation
See More
See Delta In Action





